Fractal Architect 5 Help Index
Audio Clip Curves
Applies to:FA 5
Audio Clip Curves are animation curves created from an audio sound clip. This is the easiest way to create an animation curve, but if not used correctly can lead to poor video animations.
What are Audio Clip Curves?
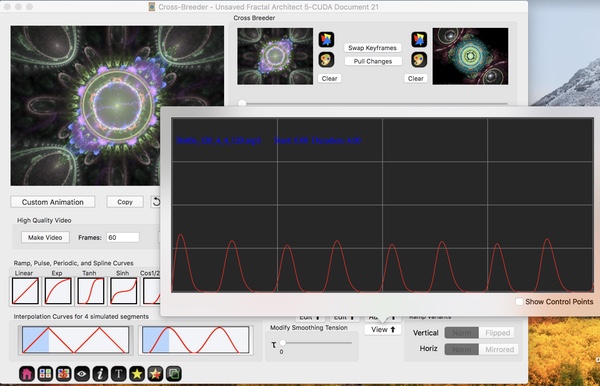
Audio clip curves are B-spline curves created from an audio waveform’s smoothed amplitude data. This curve is a good representation of the audio waveform’s amplitude envelope.
Audio Clip Smoothing Concepts
To create video animations, the animation curve is applied to fractal properties. Then each video frame, a fractal is rendered using those modified fractal properties. If motion blur is applied, then that video frame is made up of many separate rendered fractals.
The animation process samples from the animation curve(s) and modifies the initial keyframe fractal’s properties many times a second (here we are referring to the output video’s time frame, not the time it takes to render the video). A typical movie has 30 video frames per second (30 Hz).
Human beings cannot see the individual video frames at 30 Hz. We perceive a continuous flow of animation.
An average drummer beat of 120 beats per minute creates an audio signal whose main “information”, the beat, occurs at 2 Hz. Fractal animations should have “movement” of somewhere between 0.5 and 4 Hz.
Think of a dance. Everyone is moving to a beat range typically between 1 and 2 Hz. This is the frequency range where fractal video animation movement should be too, if your desire is to make the fractals “dance”.
Problem with Un-smoothed Audio Clip Curves
Audio amplitude waveforms are extremely noisy with huge jumps in value from sample to sample. Most songs have waveforms that are in the 1000 to 3000 Hz. If the app samples directly from the audio waveform, then the resulting video animations will be extremely jerky. These video animations are hard to watch – not viewer friendly.
Think of the “Information” that creates the Animation
Fractal animations from audio clips should show something extracted from the sound. This is the “information” that is so key to creating an effective animation.
For rhythmic music, this information is the “beat” of the music. For animation purposes, this beat should be represented by animation curve that looks like the beat.
Chorale singing has very little “beat” in the output sound. There is no effective way to create the original beat from a sound recording. A trained human being listening to the music can hear the underlying beat. So that human can tap a key to record the beat information that is not found in the audio recording.
Audio waveform Smoothing
The audio waveform signal is first smoothed by averaging the absolute amplitude values inside a small window of time. The size of this window is determined by the Waveform Reduction Frequency. Smoothing is inversely proportional to the reduction frequency. Low reduction frequency gives the highest smoothing and high reduction frequency gives the lowest smoothing. The default 15 Hz is a good initial setting.
In audio applications, this smoothing process is called a “low pass” filter.
Even though the beat information of 1 to 2 Hz is embedded in the sound file, you will want to use a much higher smoothing frequency (like 15 Hz) on that file.
One thing to note. Waveform smoothing eliminates the “pitch” information in the music. Pitch refers to the sound frequency information like treble and bass content.
If you want to animate pitch information visually, you will to manually create the animation spline curves.
Use Audio Click Tracks for Beat Animations
Don’t use music sound files for effective beat curves !!!
Audio clip curves extracted from music sound tracks, as a rule of thumb, make poor video animations. The key “information” needed for fractal animations is muddied by a lot of other stuff.
Even with excellent smoothing, the “motion” of the fractal animation does not represent the music well. It is hard to explain this. Try it yourself and you will see.
Simple Click Track
The best audio source for fractal animations is a musician’s click track. An another good source is the drummer’s beat track for a song, if available. You can find them online or create them yourself from an app like Garageband.
These audio clip curves are the best way to get good fractal animation curves. It is important that you set the audio clip’s start and leading silence properties, so the click track’s beat matches the music file you are animating.
Using Audio Sound Files
Audio clips are extracted from audio sound files that you choose. This does not modify the audio file. The audio clip’s waveform is read from the file. Trimming the audio clip merely changes the start and duration of the audio waveform read from the file.
Limitation: DRM protected audio files cannot be used as the source for the audio clip waveform.
See: Cross Breeder
See: Animation Concepts
See: Animation Sequencer
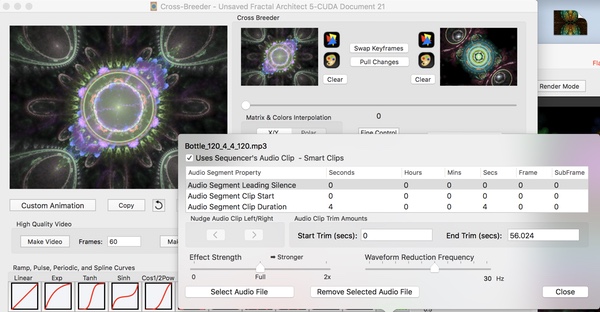
Audio Clip Curve Panel
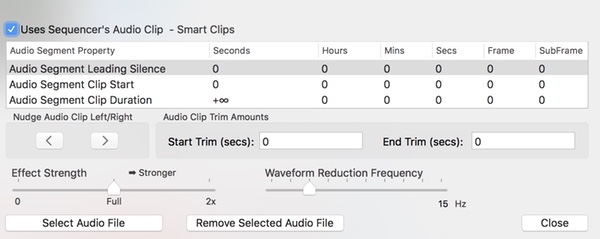
This panel allows you to select a sound file that holds the audio clip. Often only a small piece of the sound file will be used by the audio clip. The clip’s Start/Duration properties allows you to precisely specify the part you want to use.
What is SMPTE Time?
Time length is normally measured as fractional seconds. There is also the notion of SMPTE time, which is the breakdown of the total time length into integral parts:
- Hours
- Minutes
- Seconds
- Frames (Video Frames)
- SubFrames
SMPTE time is how time is represented by the movie industry and most professional audio uses it.
Audio Segment Properties Table
This table shows the 3 key parts of an audio clip:
- Its start
- Its duration
- Optional leading silence to apply
You can modify the table values by clicking on the number value in the table and then changing it.
Audio Segment Properties Table Columns
This table has columns for the property name, its time duration in fractional seconds, and then the SMPTE Time breakdown.
Example: 60.024 fractional segments has SMPTE time components of 1 minute and 58 subframes.
The table does automatic conversion from fractional seconds to SMPTE time and vice versa.
- Audio Segment Property
- Property name.
- Seconds
- The time length in fractional seconds of the audio clip.
- Hours
- SMPTE Integral number of hours of the audio clip.
- Mins
- SMPTE Integral number of residual minutes of the audio clip.
- Secs
- SMPTE Integral number of residual seconds of the audio clip.
- Frames
- SMPTE Integral number of residual video frames of the audio clip.
- Subframes
- SMPTE Integral number of residual video subframes of the audio clip.
Audio Segment Properties Table Rows
These are the 3 audio clip time related properties.
- Audio Segment Leading Silence
- Optional leading silence added before the sound starts.
- Audio Segment Clip Start
- Specifies time offset in audio file where clip starts.
- Audio Segment Clip Duration
- Specifies time duration of the audio clip.
Other Properties
- Smart Clips – (Sequencer only)
- Sequencer feature where the sequencer’s audio clip will override this one during final video renders.
Audio Clip Trim Amounts
An alternate way to trim an audio clip is by changing these Trim fields:
- Start Trim (secs)
- Trims this number of seconds from the start of file. Changes Clip Start property.
- End Trim (secs)
- Trims this number of seconds from the end of file. Changes Clip Duration property.
How to Create an Audio Clip
- Click the Audio button that opens this Audio clip panel.
- Click the Select Audio File button and select a source audio file containing the sound waveform you desire. That creates an audio clip whose start is 0 and whose duration is the time length of the audio file.
- Optional: Trim the audio clip by:
- Override the clip duration. Modify the Clip duration in the table.
- Override the clip start (to skip over leading silence embedded in the audio file – common).
- Add leading silence to the audio clip, so the animation curve has zero initial amplitude for the time you specify here.
- Optional: Or trim it by using the Start Trim and End Trim fields.
Audio Clip Smoothing
Set the ** Waveform Reduction Frequency**. Lower reduction frequency results in smoother curves. Higher reduction frequency results in noisier curves.
Experiment with your audio file to find an optimal reduction frequency.
Example
Lets load a click track. Here I have loaded the audio file “Bottle_120_4_4_120.mp3” :
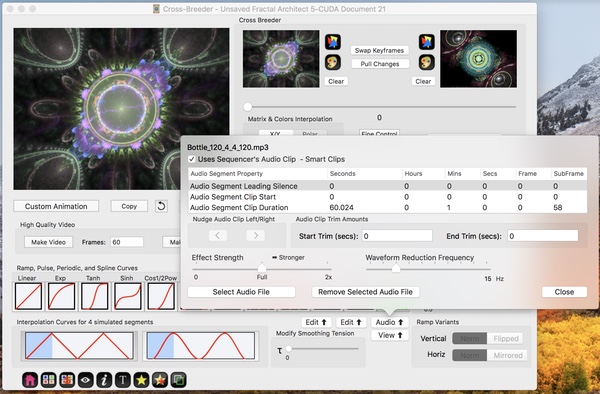
So now we have a 60 second long click track.
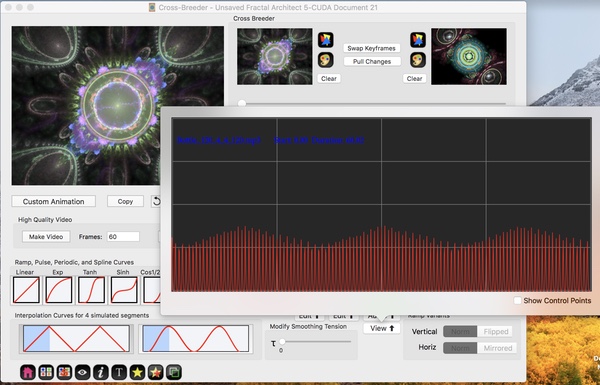
Lets trim it to 4 seconds long. Here I have overwritten the Clip Duration property.
Result: 4 second long beautiful animation curve.