Fractal Architect 5 Help Index
Transform List, Final Transform, Flame Parameters, Dimensions Panel
Applies to:FA 5
See also: Layerz & Subflames
Panel Tabs
Quick-Spin buttons
To the right of various columns and fields are the Quick-Spin buttons: 
These open the Quick-Spin windows allowing you to quickly see how that parameter affects the fractal image.
See: How to use the Quick-Spin panels
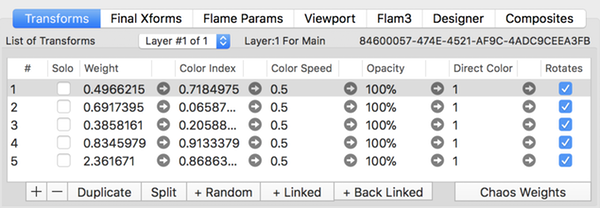
Normal Transforms List Tab
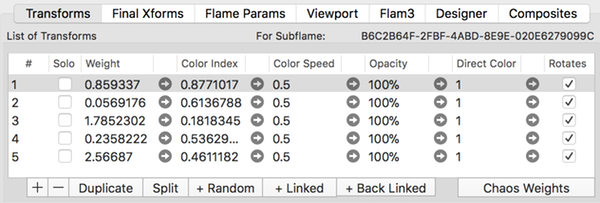
Main fractal vs Sub-flame fractal
The Transform editor can only show one fractal at a time. A basic fractal can have zero or more sub-flame variation instances. These sub-flame variation instances hold a sub-flame fractal that can be edited too.
A sub-flame fractal can itself contain other sub-flame variation instances. There is a maximum limit of 16 sub-flame nesting levels. Sub-flames cannot themselves have multiple layers.
Opening the Transform Editor for a Sub-Flame
Find the sub-flame variation instance in the parent fractal’s transform list. Click on the sub-flame variation in the Variations table. Click on the Transform editor button to open the transform editor for the sub-flame’s fractal.
Active Layer Selection
The Transform editor can only show one basic fractal at a time. In FA 5, a composite multi-fractal can have more than one basic fractal. You should use the fractal’s Info view to see how the fractal is constructed. Each basic fractal has its own unique UUD (32 digit hexadecimal number). The current basic fractal’s UUID is shown here.
The Transform editor can only show one layer’s fractal at a time. You can change the active layer using the popup menu. The layer’s fractal UUID is show too.
Column Definitions
- Solo
- When set hides the all transforms but this one are hidden in the fractal image. (Not a permanent setting - use Opacity instead.)
- Weight (Quick-Spin capable)
- The relative weight for this transform.
- Color Index (Quick-Spin capable)
- Index into Color Gradient color values for this transform.
- Color Speed (Quick-Spin capable)
- How rapidly the effective color index changes between iterations.
- Opacity (Quick-Spin capable)
- Alpha value for this transform.
- Direct Color (Quick-Spin capable)
- Amount of direct coloring to apply. Range is 0 to 1.
Only works with variation types that provide direct coloring support. - Rotates
- Indicates whether this transform can be animated.
Transform List Buttons
- +
- Add new linear transform with identity pre and post **matrices.
- -
- Delete the selected transform.
- Duplicate
- Adds a new transform that is an identical copy of the selected transform.
- Split
- Splits a transform into two identical transforms except for their weights which will be half of the original transform’s weight.
- + Random
- Adds a new randomized transform with random variations and matrices.
- + Linked
- Adds a new linked linear transform that is linked to the currently selected transform by chaos.
(The chaos weight from the selected transform to the new transform is 100% and 0% to all others.) - + Back Linked
- Adds a new linked linear transform that is back linked to the currently selected transform by chaos.
(The chaos weight to the selected transform from the new transform is 100% and 0% to all others.) - Chaos Weights
- Adjust the chaos weights for the selected transform.More
Triangle Editor and Layerz
The Triangle editor can only edit one layer at a time.
Switching Between Layers
Near the top of the Triangle editor is the Layer Select popup menu button. Use that to switch over to editing other layers.
Layer Labeling
The current layer (the one you are looking at now) fractal’s Triangle editor instance shows a Layer Select popup menu, then the current layer number, then the text “For Main”, then this layer’s Uuid.
Final Transforms Tab
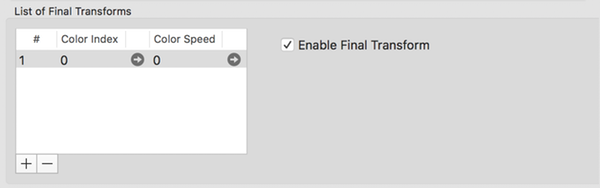
A final transform is applied to the point pool immediately after the ordinary transforms are applied. Many fractals do not use a final transform. They must be explicitly enabled.
FA 5 introduces support for multiple final transforms, they are applied in series. Final transforms can themselves contain sub-flame variations. In that case, the final transform becomes a “final fractal”.
Column Definitions
- Color Index (Quick-Spin capable)
- Index into Color Gradient color values for this transform.
- Color Speed (Quick-Spin capable)
- How rapidly the effective color index changes between iterations.
Final Transforms List Buttons
- +
- Add new empty final transform with identity pre and post **matrices.
- -
- Delete the selected final transform.
Field Definitions
- Enable Final Transforms
- Show / hide final transforms.
Flame Parameters Tab
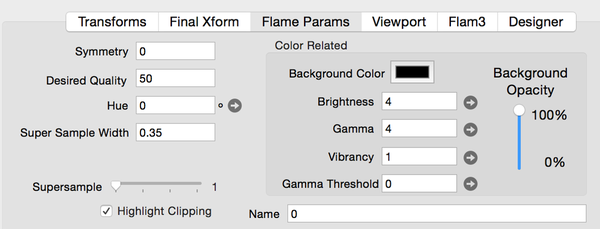
Field Definitions
- Symmetry
- Fractal symmetry. Integer value >1 implies image rotaional symmetry of same amount. Negative values are dihedral symmetry.
- Desired Quality
- Number of iterations per pixel.
- Hue (Quick-Spin capable)
- Color Hue offset from the color gradient definition (in degrees)
- Super Sample Width
- Flam4 anti-aliasing width in pixels (can be fractional).
- Background Color
- The background color for the fractal image.
- Brightness (Quick-Spin capable)
- Image brightness
- Gamma (Quick-Spin capable)
- Gamma value for flame fractal tone mapping
- Vibrancy (Quick-Spin capable)
- Color vibrancy.
- Gamma Threshold (Quick-Spin capable)
- Gamma linearization threshold.
- Background Opacity
- Opacity of fractal image (inverse of transparency).
- Name
- Name for this fractal.
- Filter
- Flam3 kernel size multiplier for supersampled image reduction.
- Supersample
- Flam3 Supersample multiplier. The fractal’s effective render size is supersample X image size. Used in conjunction with the filter setting to help control anti-alias high density areas of the fractal. Values greater than 1 greatly increase render times.
- Highlight Clipping
- Turns Highlight clipping on or off. Simplified Flam3 Highlight power setting.
Clipping manifests itself as color shifts in high density areas. Clipped colors tend toward cyan, magenta, yellow, or white. See Highlight Power explanation for more info.
Viewport Tab
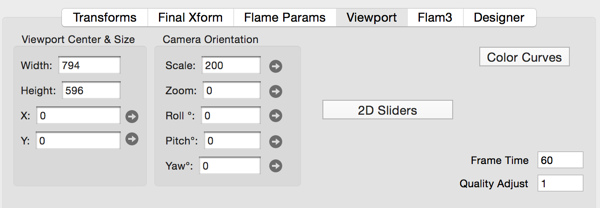
Field Definitions
- Width
- Fractal image width in pixels - the value to be stored in the file.
- Height
- Fractal image height in pixels - the value to be stored in the file.
- X (Quick-Spin capable)
- View camera center: x
- Y (Quick-Spin capable)
- View camera center: y
- Scale (Quick-Spin capable)
- View camera scale factor.
- Zoom (Quick-Spin capable)
- Scale the fractal by this power of 2. Also adjusts quality to compensate for zoom amount.
- Pitch (Quick-Spin capable)
- Adjusts the camera pitch (range 0 to 180 degrees).
- Yaw (Quick-Spin capable)
- Adjusts the camera yaw (range 0 to 360 degrees).
- Roll (Quick-Spin capable)
- Adjusts the camera roll. (range 0 to 360 degrees)
When pitch and yaw are equal to 0, roll has the same effect as 2d rotation. - DOF (Depth-of-Field) (Quick-Spin capable)
- Adjusts the artificial depth-of-field. (range of 0.0 to 1.0)
(The fractal is sharp at the point of focus and becomes blurred the further its points are from the center of focus - see Camera Height) - Perspective (Quick-Spin capable)
- Adjust for Perspective distortion (range of 0.0 to 1.0)
Perspective of 0 is no distortion. Perspective of 1 is maximum distortion. - Camera Height (Quick-Spin capable)
- Adjust the distance from the camera to the point of focus. Used together with DOF.
Viewport Tab - 3D Camera Settings
See: 3D Fractals for detailed explanation of the many 3D camera settings.
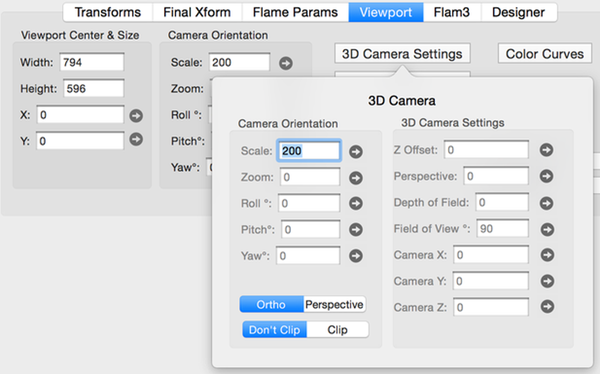
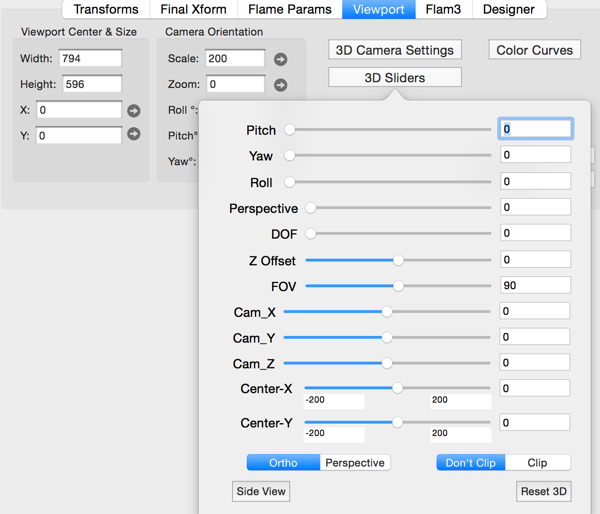
The 3D viewing camera has these parameters:
- Pitch
- Adjusts the camera pitch (range 0 to 180 degrees).
- Yaw
- Adjusts the camera yaw (range 0 to 360 degrees).
- Roll
- Adjusts the camera roll. (range 0 to 360 degrees)
When pitch and yaw are equal to 0, roll has the same effect as 2d rotation. - DOF (Depth-of-Field)
- Adjusts the artificial depth-of-field. (range of 0.0 to 1.0)
(The fractal is sharp at the point of focus and becomes blurred the further its points are from the center of focus - see Camera Height) - Perspective
- Adjust for Perspective distortion (range of 0.0 to 1.0)
Perspective of 0 is equivalent to Orthographic projection. Perspective of 1 is equivalent to normal Perspective projection. - Camera Height
- Adjust the distance from the camera to the point of focus. Used together with DOF.
Additional Free Camera Settings
Fractal Architect extends the classical Apophysis 3D Hack camera to make it better support 3D animations.
- Camera X, Y, Z Eyepoint Location
- Adjusts the camera’s eyepoint in the fractal world coordinates.
- Camera FOV (Field-of-View)
- Adjusts the camera’s Field of View of the camera frustum.
- Camera Clip
- Clip clips out points behind the camera.
- Don’t Clip does not clip points behind the camera. Apophysis 3D Hack mode
- Camera Ortho / Perspective
- sets camera viewing behavior to either full Orthographic projective or full Perspective projective.
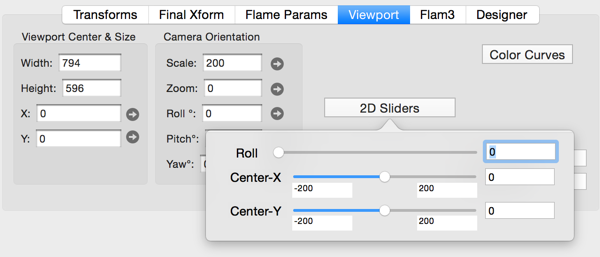
Viewport Tab - 2D Camera Settings
The 2D camera settings are much simpler.
Supplemental Color Curves
Fractal Architect 5 fractals can utilize supplemental color curves. These operate much like the color curve editors in popular photo editor apps where you can manipulate the separate RGB, Red, Green, and Blue color curves.
Click the mouse on top of the color curve to insert a new control point, then drag it to shape the curve.
If the mouse is clicked close to an existing control point, it will be selected so you can drag it with the mouse to shape the curve.
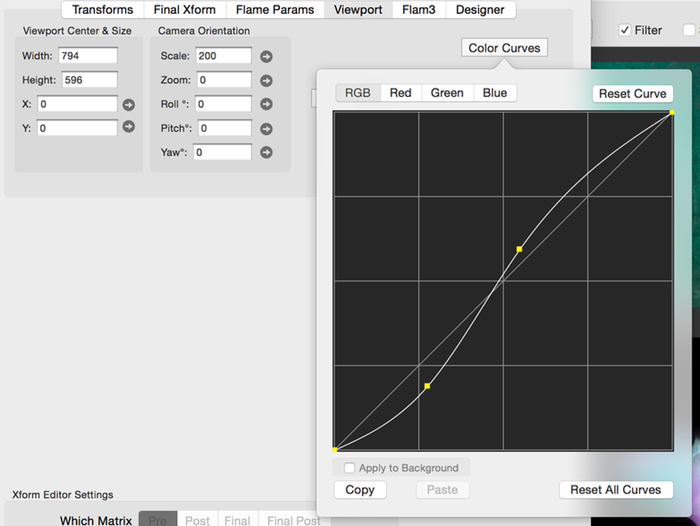
- RGB, Red, Blue, and Green Curve Selector
- Selects which color curve to show in the color curve editor.
- Reset Curve
- Resets the curve shown to simple straight line.
- Reset All Curves
- Resets all 4 curves to simple straight line.
- Apply To Background
- If selected, applies the color curves to the fractal’s background color too.
- Copy
- Copy the color curves definition to the clipboard.
- Paste
- Paste the color curves definition from the clipboard.
Flam3 Tab
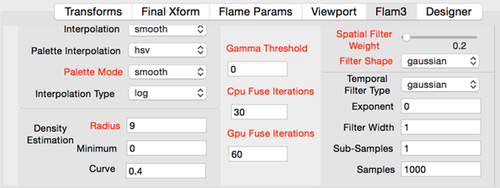
These rarely need to be modified, so you can just use the default values. See Flam3 File format specification for more info.
Field Definitions
Only fields whose name is printed with red apply to Fractal Architect.
- Interpolation
- How fractals interpolate over time. Choose either smooth or linear.
- Palette Interpolation
- Method for interpolating between color maps. Choose either hsv or sweep.
- Palette Mode
- How to interpolate between color map entries. Choose either step or linear.
- Interpolation Type
- Method for interpolating transform positions. Choose from log, linear, or old.
- Gamma Threshold
- Linearization threshold.
- CPU Fuse Iterations
- Number of iterations for when fuse is finished for a point (applies to CPU rendering).
- GPU Fuse Iterations
- Number of iterations for when fuse is finished for a point (applies to GPU rendering).
- Filter
- Kernel size multipler for supersampled image reduction.
- Spatial Filter Weight
- Spatial filter weight.
- Filter Shape
- Shape of the reduction filter. Choose from gaussian, hermite, box, triangle, bspline, mitchell, blackman, hanning, hamming, or quadratic.
- Temporal Filter Type
- Temporal kernel type for motion blur. Choose from box, exp, or gaussian.
- Exponent
- For exp temporal filter type, controls direction and rate of motion.
- Filter Width
- Length of motion blur in units of frames.
- Sub-Samples
- Number of temporal sub-samples. See Flam3 File format specification for more info.
- Samples
- Number of time samples used in motion blur.
Designer Tab
Field Definitions
- URL
- Designer’s URL info (optional). Embedded into file.
- Nickname
- Designer’s Nickname or name info (optional). Embedded into file.